SimpleCPU
The SimpleCPU is a purely functional, in-order model that is suited for cases where a detailed model is not necessary. This can include warm-up periods, client systems that are driving a host, or just testing to make sure a program works.
It has recently been re-written to support the new memory system, and is now broken up into three classes.
BaseSimpleCPU
The BaseSimpleCPU serves several purposes:
- Holds architected state, stats common across the SimpleCPU models.
- Defines functions for checking for interrupts, setting up a fetch request, handling pre-execute setup, handling post-execute actions, and advancing the PC to the next instruction. These functions are also common across the SimpleCPU models.
- Implements the ExecContext interface.
The BaseSimpleCPU can not be run on its own. You must use one of the classes that inherits from BaseSimpleCPU, either AtomicSimpleCPU or TimingSimpleCPU.
AtomicSimpleCPU
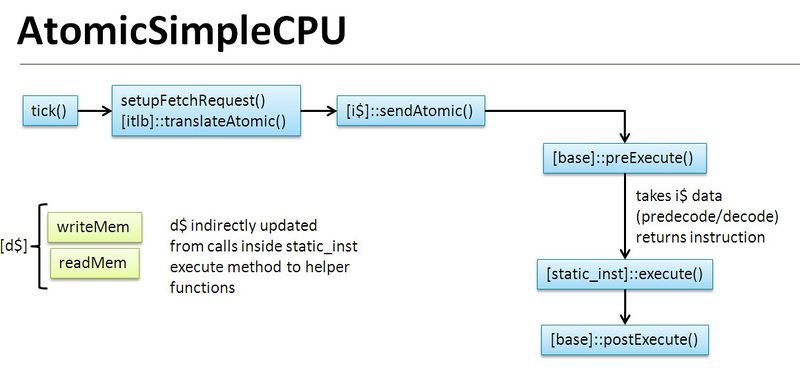
The AtomicSimpleCPU is the version of SimpleCPU that uses atomic memory accesses (see Memory System for details). It uses the latency estimates from the atomic accesses to estimate overall cache access time. The AtomicSimpleCPU is derived from BaseSimpleCPU, and implements functions to read and write memory, and also to tick, which defines what happens every CPU cycle. It defines the port that is used to hook up to memory, and connects the CPU to the cache.
TimingSimpleCPU
The TimingSimpleCPU is the version of SimpleCPU that uses timing memory accesses (see Memory System for details). It stalls on cache accesses and waits for the memory system to respond prior to proceeding. Like the AtomicSimpleCPU, the TimingSimpleCPU is also derived from BaseSimpleCPU, and implements the same set of functions. It defines the port that is used to hook up to memory, and connects the CPU to the cache. It also defines the necessary functions for handling the response from memory to the accesses sent out.